TA的每日心情 | 开心
2019-11-4 13:48 |
|---|
签到天数: 14 天 连续签到: 1 天 [LV.3]偶尔看看II
|
如何通过树莓派的GPIO接口控制步进电机
1、实验目的
在树莓派上编写一个C程序,通过其GPIO口控制步进电机的转动方向以及速度。
2、为什么要用树莓派来控制步进电机
在我的概念中,无论是控制接在树莓派上的摄像头来拍照,还是通过树莓派控制LED发光,我都还是在“虚拟世界”中折腾树莓派,因为它没有向外界输出任何动作。而在构建一个稍微复杂的系统时,这种能力可能是很重要的,于是,用树莓派来控制步进电机是我必须要做的事情。
3、实现方案
怎样通过Raspberry Pi的GPIO口来控制步进电机?已经有很多人这样做了。由于步进电机通常需要一块驱动板,而这样的产品已经很容易买到并且极其廉价(肯定比你自己做要便宜),因此,我们没有必要自己去做。我在淘宝上不断地查啊查,终于找到了白菜价的步进电机和配套驱动板,加起来才一共8块多钱。
下面来看看我买的步进电机和驱动板的样子:

步进电机和驱动板的接线:

该驱动板配有一个原理图,根据它我们可以知道如何把整个系统连接起来:

可见,驱动板上有4个输入口:IN1~IN4,这4个口用来接树莓派的4个GPIO口。同时,我们需要为驱动板提供5V的供电,这从哪里来?当然是从树莓派引出来。从下面的GPIO口分布图可以得知,“2”口就是+5V,正好就利用它。
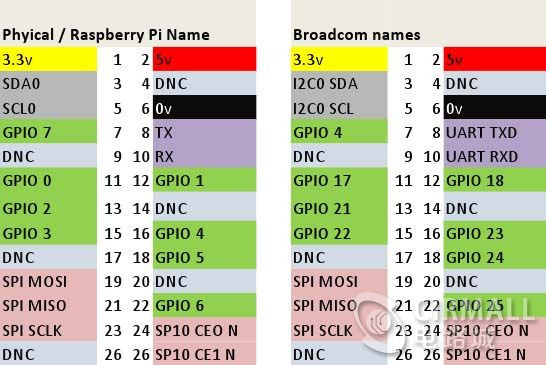
我将树莓派上的GPIO 17、18、21、22口(用树莓派的命名方式就是0、1、2、3口)分别接到步进电机驱动板上的IN1、IN2、IN3、IN4口,最后接好线的效果如下:

4、编写程序
在参考了这款步进电机配套的51单片机的示例代码后,我知道了依次把驱动板的IN1~IN4置为高电平,就可以驱动步进电机,也就是说,要把树莓派的4个GPIO输出口依次置为高电平。例如,假设用0代表低电平,1代表高电平的话,GPIO 17、18、21、22口的电平第一次被置为1、0、0、0,第二次被置为0、1、0、0,第三次被置为0、0、1、0,第四次被置为0、0、0、1。
于是我写出了下面的代码(仍然使用WiringPi这个库来操作GPIO):
- /* moto.c
- * A program to control a stepper motor through the GPIO on Raspberry Pi.
- *
- * Author: Darran Zhang (http://www.codelast.com)
- */
- #include <wiringPi.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #define clockWISE 1
- #define COUNTER_CLOCKWISE 2
- void delayMS(int x);
- void rotate(int* pins, int direction);
- int main(int argc,char* argv[]) {
- IF (argc < 4) {
- printf("Usage example: ./motor 0 1 2 3 \n");
- return 1;
- }
- /* number of the pins which connected to the stepper motor driver board */
- int pinA = atoi(argv[1]);
- int pinB = atoi(argv[2]);
- int pinC = atoi(argv[3]);
- int pinD = atoi(argv[4]);
- int pins[4] = {pinA, pinB, pinC, pinD};
- if (-1 == wiringPiSetup()) {
- printf("Setup wiringPi failed!");
- return 1;
- }
- /* set mode to output */
- pinMode(pinA, OUTPUT);
- pinMode(pinB, OUTPUT);
- pinMode(pinC, OUTPUT);
- pinMode(pinD, OUTPUT);
- delayMS(50); // wait for a stable status
- for (int i = 0; i < 500; i++) {
- rotate(pins, CLOCKWISE);
- }
- return 0;
- }
- /* Suspend execution for x milliseconds intervals.
- * @param ms Milliseconds to sleep.
- */
- void delayMS(int x) {
- usleep(x * 1000);
- }
- /* Rotate the motor.
- * @param pins A pointer which points to the pins number array.
- * @param direction CLOCKWISE for clockwise rotation, COUNTER_CLOCKWISE for counter clockwise rotation.
- */
- void rotate(int* pins, int direction) {
- for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
- if (CLOCKWISE == direction) {
- for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
- if (j == i) {
- digitalWrite(pins[3 - j], 1); // output a high level
- } else {
- digitalWrite(pins[3 - j], 0); // output a low level
- }
- }
- } else if (COUNTER_CLOCKWISE == direction) {
- for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
- if (j == i) {
- digitalWrite(pins[j], 1); // output a high level
- } else {
- digitalWrite(pins[j], 0); // output a low level
- }
- }
- }
- delayMS(4);
- }
- }
[color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]复制代码
编译程序:
[color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]复制代码
- g++ motor.c -o motor -lwiringPi
[color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]复制代码
运行程序:
[color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]复制代码
这里向程序传入了4个参数,它们分别代表要控制的树莓派的GPIO口。切记,由于使用了WiringPi库,所以要参考上面的GPIO分布图的左边那部分来确定这些数字。
可以看到步进电机已经转动了(如下面的Youku视频所示)。如果你发现转动方向(顺/逆时针)反了,你可以把传入的参数顺序调整一下,就可以让它转对方向。
从前面的代码可见,如果要改变步进电机的转速,只需要改变rotate()函数中每次delay的时间即可。因此,如果我们把delay的时间逐渐由大变小,就会导致步进电机呈加速状态。让步进电机周期性加速的完整代码如下:
- /* motor_speed_up.c
- * A program to control a stepper motor(speed up) through the GPIO on Raspberry Pi.
- *
- * Author: Darran Zhang (http://www.codelast.com)
- */
- #include <wiringPi.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #define CLOCKWISE 1
- #define COUNTER_CLOCKWISE 2
- void delayMS(int x);
- void rotate(int* pins, int direction, int delay);
- void stop(int* pins);
- int main(int argc,char* argv[]) {
- if (argc < 4) {
- printf("Usage example: ./motor 0 1 2 3 \n");
- return 1;
- }
- /* number of the pins which connected to the stepper motor driver board */
- int pinA = atoi(argv[1]);
- int pinB = atoi(argv[2]);
- int pinC = atoi(argv[3]);
- int pinD = atoi(argv[4]);
- int pins[4] = {pinA, pinB, pinC, pinD};
- if (-1 == wiringPiSetup()) {
- printf("Setup wiringPi failed!");
- return 1;
- }
- /* set mode to output */
- pinMode(pinA, OUTPUT);
- pinMode(pinB, OUTPUT);
- pinMode(pinC, OUTPUT);
- pinMode(pinD, OUTPUT);
- delayMS(50); // wait for a stable status
- int delay = 25;
- while (true) {
- for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
- rotate(pins, CLOCKWISE, delay);
- }
- delay--;
- if (delay < 4) {
- delay = 25;
- stop(pins);
- delayMS(500);
- }
- }
- return 0;
- }
- /* Suspend execution for x milliseconds intervals.
- * @param ms Milliseconds to sleep.
- */
- void delayMS(int x) {
- usleep(x * 1000);
- }
- /* Rotate the motor.
- * @param pins A pointer which points to the pins number array.
- * @param direction CLOCKWISE for clockwise rotation, COUNTER_CLOCKWISE for counter clockwise rotation.
- * @param delay The time intervals(in ms) to delay, and if the value is smaller, the motor rotates faster.
- */
- void rotate(int* pins, int direction, int delay) {
- for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
- if (CLOCKWISE == direction) {
- for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
- if (j == i) {
- digitalWrite(pins[3 - j], 1); // output a high level
- } else {
- digitalWrite(pins[3 - j], 0); // output a low level
- }
- }
- } else if (COUNTER_CLOCKWISE == direction) {
- for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
- if (j == i) {
- digitalWrite(pins[j], 1); // output a high level
- } else {
- digitalWrite(pins[j], 0); // output a low level
- }
- }
- }
- delayMS(delay);
- }
- }
- /* Stop the motor.
- * @param pins A pointer which points to the pins number array.
- */
- void stop(int* pins) {
- for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
- digitalWrite(pins, 0); // output a low level
- }
- }
[color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]复制代码
|
|
|
 /1
/1 
 /1
/1 